BREAKING: HHS' Top Medical Officer Blasts mRNA Vaccines As Dangerous Experiments
Folks, the mRNA vaccine scam is unraveling, and a top HHS insider is spilling the truth. Dr. Steven Hatfill, senior medical advisor at the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), just gave an explosive interview with Dana Parish. He’s a virologist and biodefense expert, serving as a special advisor in the Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response (ASPR) under HHS Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. since early this month. He also worked in the first Trump administration. Hatfill’s seen the cover-ups firsthand, and he’s calling out the mRNA vaccines for what they are: a dangerous experiment.
"We’re not seeing a dramatic cancer association with the virus, but we are with the vaccinated people!"
Dr. Steven Hatfill, HHS Special Medical Advisor
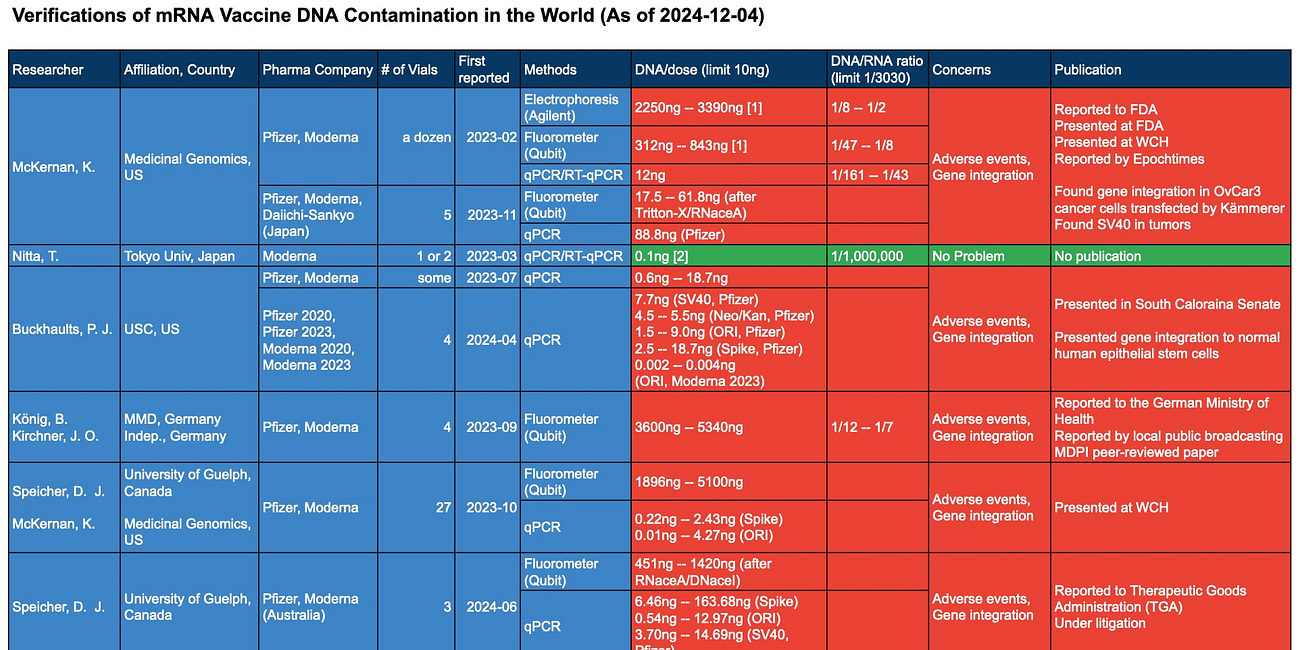
Dr. Hatfill is crystal clear about one of the mRNA vaccine’s dirtiest secrets: the SV40 enhancer. He knows this genetic “afterburner” supercharges gene expression, like slamming the gas on a car with no brakes. It’s a disaster waiting to happen. The vaccines also contain plasmid DNA, and your cells’ LINE-1 mechanism grabs this foreign DNA, shoving it into your chromosomes. These “jumping genes” can land next to cancer-related genes, triggering chaos. Dr. Hatfill’s aware that the SV40 enhancer makes this worse, amplifying genes that can turn your body into a tumor factory. Random insertions disrupt pre-oncogenes, leading to cancer. Studies show spike protein from the VACCINE—not the virus—in tumors, months after the jab. “We’re not seeing a dramatic cancer association with just the virus,” Hatfill says. “But we are with the vaccinated people.” Autopsy data and published papers confirm it. This is real, and it’s terrifying.
They told you the vaccine stays in your arm. Dr. Hatfill says that’s a lie. The Japanese Health Ministry sued Pfizer and got the data. They marked the vaccine with fluorescent dye and saw it spread to 20 organs in rats—within MINUTES. Your liver, heart, brain, ovaries—everywhere. They knew it and pushed the lie anyway. Why? Money talks.
Then there’s the lipid nanoparticles, the mRNA delivery system. They don’t just drop off the spike protein. They disrupt cells, trigger allergic reactions, and damage organs like the heart. They contain polyethylene glycol—antifreeze. The spike protein itself is toxic, making your body attack itself. “You’re making your own poison if you’re vaccinated,” Hatfill says. This wasn’t a vaccine. It was a reckless experiment.
Hatfill’s adamant: these mRNA shots were highly experimental. Nothing like this had ever been tested on humans at this scale. The clinical trials? A sick joke. They skipped old people, pregnant women, and babies, cherry-picking fit, healthy folks in their prime. Even then, problems piled up—data “misplaced” or swept under the rug. Pfizer tried to bury their trial data for 70 YEARS, despite laws demanding immediate release after emergency use authorization. “Do you remember that debacle?” Hatfill asks. They gambled with your life on untested tech, and the results are catastrophic.
A population collapse in mRNA Vaccinated People?
The fallout is brutal. Young men are losing testosterone—vaccine damage to their gonads. Women? Spike protein is piling up in their ovaries, and infertility is surging. Hatfill’s working with gynecologists (ABRG) on studies to examine ovarian reserve in vaccinated college women, and we’ll know the full damage soon. Just look at the recent study Nicolas Hulscher highlighted on May 9, 2025: rats given human-equivalent mRNA doses lost over 60% of their primordial follicles—permanent damage to the egg supply. AMH levels crashed, dying follicles spiked, and inflammation markers like TGF-β1 soared.
BREAKING: COVID-19 mRNA Shots Destroy Over 60% of Women’s Non-Renewable Egg Supply
2 months ago · 335 likes · 105 comments · Nicolas Hulscher, MPH
If this holds true for humans, we’re talking early menopause and infertility on a massive scale. Hatfill is working with Advanced Biological Research Group to dig deeper, and the numbers could be devastating. Pregnant women? The American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology took $11 million and declared the vaccines safe—while ignoring miscarriages. “They didn’t count the miscarriages, did they?” Hatfill asks. The trimester you get jabbed in changes the effects, but they didn’t care.
The culprits: Fauci, Peter Marks, Janet Woodcock, and editors of the New England Journal of Medicine and The Lancet. A “handful of federal bureaucrats” who did the wrong thing. Greed, conflicts of interest, and Big Pharma’s billions twisted science. Faulty papers claimed hydroxychloroquine didn’t work—it did. The CDC pushed vaccines on pregnant women. Fauci’s still writing papers in 2025 claiming the vaccines were “safe and wonderful.” Hatfill wouldn’t touch it. Are they protected by the PREP Act? Some might be, but Hatfill hints at autopen-signed pardons and a million dead Americans(I reckon its way more!). “How much was due to incompetence? How much was due to greed?”
Hatfill’s disillusionment hits hard. “I always thought being a doctor was the best thing I could be,” he says. “You follow the rules, you’ve got ethics, and it can be bought.” He’s scarred, watching the medical establishment sell out. We’re all reeling from the betrayal.
This is a wake-up call. The mRNA vaccines are dangerous. Cancer, infertility, organ damage, and a corrupt medical system. The evidence is growing, and the truth won’t stay buried. Share this everywhere. Demand answers. The Medical Mafia’s days are numbered. Stay angry, stay informed, and let’s fight back together.
Thanks to Dana Parish for the interview! The full video is avalable here!
Dr. Steven Hatfill: From Anthrax Exoneration to Top Rank at HHS
2 months ago · 10 likes · 5 comments · Dana Parish
Signing off for now
A17
Thanks for reading PharmaFiles by Aussie17! This post is public so feel free to share it.
https://open.substack.com/pub/pharmafiles/p/breaking-hhs-top-medical-officer?r=1p9ueh&utm_medium=ios